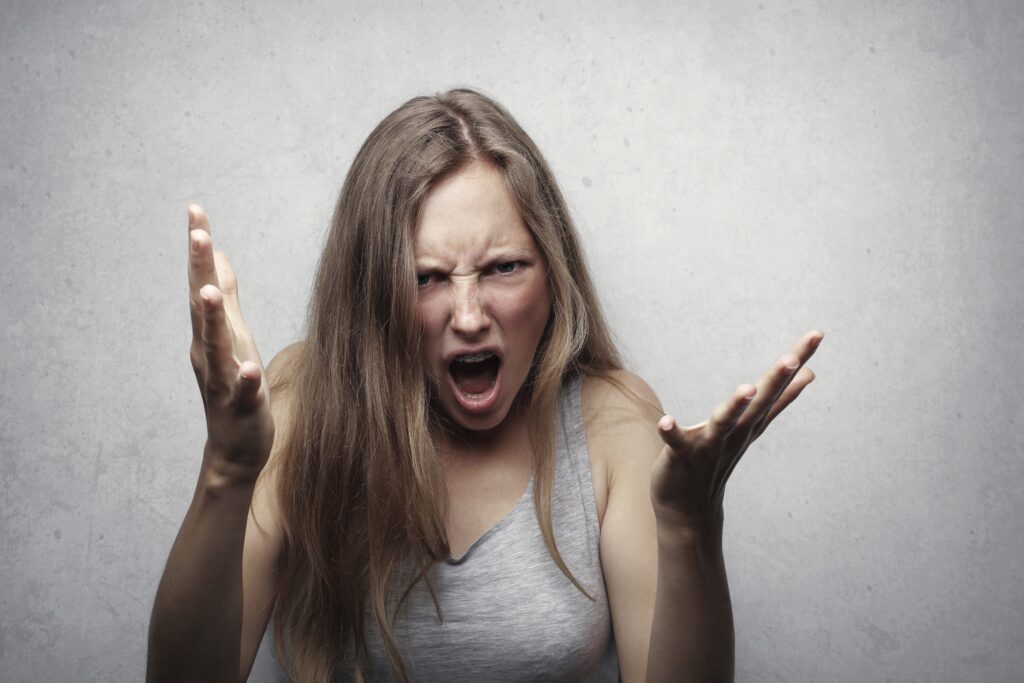
Lying is a common behavior in childhood, and understanding why kids lie to their parents is crucial for parents, educators, and psychologists. Lying is a complex and multifaceted behavior that serves various functions in human interactions. In childhood, lying is a common occurrence, with many children engaging in deceptive behaviors at some point in their development. Understanding why kids lie to their parents is essential for parents, educators, and psychologists to promote honesty and integrity in children’s behavior.
Developmental Factors
Children often lie in their developmental stages. In early childhood, around 3-4, children start to understand the concept of lying and its consequences. They may lie to avoid punishment or to protect themselves from disapproval. As children grow older, their lies become more sophisticated, reflecting their developing cognitive skills and emotions, such as theory of mind and perspective-taking. Older children may lie to protect their privacy, avoid embarrassment, or manipulate their parent’s perceptions.
Social Influences
Social factors also play a significant role in children’s lying behavior. Children learn about lying from observing others, including their parents, siblings, and peers. They may lie to imitate behaviors they see in others or to conform to social expectations. Peer pressure can also influence children’s lying behavior, as they may lie to fit in with their peers or avoid social rejection.
Individual Differences
Individual differences in personality and temperament can also contribute to children’s lying behavior. Some children may be more impulsive or sensation-seeking, leading them to engage in more deceptive behaviors. Others may be more anxious or fearful, leading them to lie to avoid negative consequences or criticism. Additionally, children who have experienced trauma or stress may be more likely to lie as a coping mechanism.


Parenting Styles
Parenting styles can have a significant impact on children’s honesty. Proper parenting, which is characterized by warmth, support, and reasonable expectations, is associated with higher levels of honesty in children. In contrast, authoritarian parenting, which is characterized by strict rules and harsh discipline, may lead to higher levels of lying as children seek to avoid punishment. Permissive parenting, which is characterized by lenient rules and a lack of discipline, may also contribute to higher levels of lying as children do not learn the importance of honesty and integrity.
Strategies for Fostering Honesty
Parents, educators, and psychologists can take several steps to foster honesty in children. First, they can model honest behavior themselves, as children learn by observing others. Second, they can praise and reward honest behavior, reinforcing the value of honesty. Third, they can create a supportive and non-judgmental environment where children feel comfortable expressing themselves truthfully. Finally, they can teach children about the importance of honesty and the consequences of lying, helping them understand the impact of their actions on themselves and others.
Conclusion
Understanding why kids lie to their parents is essential for promoting honesty and integrity in children’s behavior. Developmental factors, social influences, individual differences, and parenting styles all play a role in shaping children’s lying behavior. By understanding these factors and implementing strategies to foster honesty, parents, educators, and psychologists can help children develop into truthful and trustworthy individuals.
References
Lewis, M., Stanger, C., & Sullivan, M. W. (1989). Deception in 3-year-olds. Developmental psychology, 25(3), 439.
Talwar, V., & Lee, K. (2008). Social and cognitive correlates of children’s lying behavior. Child development, 79(4), 866-881.
Darling, N., & Steinberg, L. (1993). Parenting style as context: An integrative model. Psychological bulletin, 113(3), 487.
Heyman, G. D., & Legare, C. H. (2005). Children’s beliefs about lie-telling and its relation to their actual lie-telling behavior. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 29(1), 35-41.
FAQ
How to handle when your child lies to you?
When your child lies, address the behavior calmly and discuss the importance of honesty. Encourage them to tell the truth by creating a safe environment. Avoid harsh punishment, instead focus on building trust and understanding why they felt the need to lie.
How do you discipline a child for lying?
Parents and educators can take several steps to foster honesty in children. First, they can model honest behavior themselves, as children learn by observing others. Second, they can praise and reward honest behavior, reinforcing the value of honesty. Third, they can create a supportive and non-judgmental environment where children feel comfortable expressing themselves truthfully. Finally, they can teach children about the importance of honesty and the consequences of lying, helping them understand the impact of their actions on themselves and others.
How do be gentle parent to a child who lies?
Proper parenting, which is characterized by warmth, support, and reasonable expectations, is associated with higher levels of honesty in children. In contrast, authoritarian parenting, which is characterized by strict rules and harsh discipline, may lead to higher levels of lying as children seek to avoid punishment.
FOLLOW US ON




Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://www.binance.com/si-LK/register?ref=LBF8F65G
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://accounts.binance.com/ES_la/register-person?ref=VDVEQ78S
Càng tham gia lâu dài và tích cực, người tham gia sẽ càng được hưởng những ưu đãi lớn hơn. 888SLOT Các thành viên VIP của nhà cái thường nhận được phần quà đặc biệt, tỷ lệ hoàn tiền cao hơn, cả những ưu đãi cá nhân hóa như quản lý tài khoản riêng, hỗ trợ ưu tiên cùng nhiều quyền lợi khác. TONY01-12
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://accounts.binance.info/si-LK/register-person?ref=LBF8F65G
188V sở hữu bản quyền phát sóng trực tiếp các giải bóng đá lớn, cho phép quý khách vừa theo dõi vừa đặt cược trực tiếp. TONY01-25H
Chính sách hoàn trả không giới hạn của 188V được đánh giá là cạnh tranh nhất thị trường, giúp tối ưu hóa lợi ích tài chính cho người chơi trong mỗi phiên cược. TONY01-25
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.com/pt-BR/register?ref=GJY4VW8W
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://accounts.binance.info/da-DK/register?ref=V3MG69RO
Nạp tiền qua ví điện tử tại 188V nhận thêm 5% giá trị mỗi lần nạp. Khuyến mãi áp dụng xuyên suốt dành cho tất cả thành viên. TONY02-25O